This is a sleep disorder characterized by interruptions in breathing during sleep. Explain that these interruptions, known as apneas, can result from either a partial or complete blockage of the upper airway (obstructive sleep apnea) or a failure of the brain to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing (central apnea).
Causes and symptoms of Sleep Apnea:
Emphasize the significance of understanding apnea’s causes and symptoms to promote early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Untreated apnea can have serious consequences for overall health and well-being.

Effective treatment options for Sleep Apnea:
There are several treatment options available for
1- Including lifestyle modifications
2-Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy
3-Oral appliances
4-Surgical interventions
Highlight that the choice of treatment depends on the type and severity of sleep apnea.
Types of Sleep Apnea:
Provide a more detailed explanation of the different types of Apnea
1-Obstructive Sleep Apnea
2-Central Sleep Apnea
3-Mixed Sleep Apnea
Prevalence and demographics of Sleep Apnea
Noting that it affects a significant portion of the population. Highlight any demographic factors that may increase the risk of developing sleep apnea, such as age, gender, obesity, and certain medical conditions.
Risk factors and potential complications
The various risk factors associated with apnea, such as obesity, smoking, family history, and certain anatomical factors. The potential complications that can arise from untreated apnea, including cardiovascular problems, metabolic disorders, and cognitive impairments.
Causes of Obstructive sleep apnea: Obstructive apnea occurs due to a physical blockage of the upper airway during sleep. The role of various factors, such as obesity, enlarged tonsils, nasal congestion, and structural abnormalities, in contributing to airway obstruction.
Causes of Central sleep apnea: Central sleep apnea results from a dysfunction in the central nervous system, specifically the brain’s respiratory control centers.Underlying medical conditions, such as heart failure, stroke, and brainstem lesions, can lead to central apnea.
Causes of Mixed sleep apnea: This is a combination of both obstructive and central apnea. This type of apnea presents unique challenges in terms of diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea
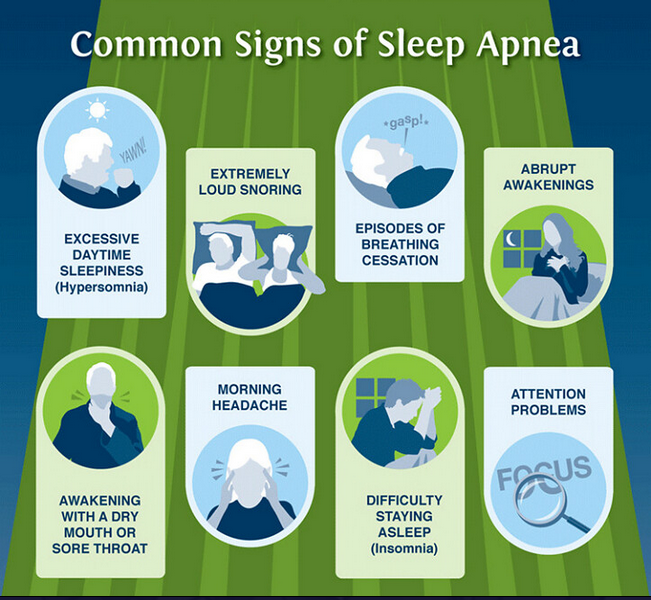
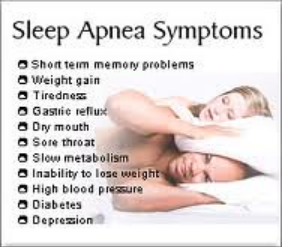
Common symptoms: The common symptoms experienced by individuals with apnea, including loud snoring, excessive daytime sleepiness, morning headaches, dry mouth or sore throat upon waking, and irritability.
Diagnostic methods: Diagnostic methods used to confirm apnea, including overnight sleep studies (polysomnography), home sleep apnea testing, and the use of portable monitoring devices. These tests monitor various physiological parameters during sleep to determine the presence and severity of apnea.
Health Risks and Complications of Sleep Apnea
Severity classification: The classification of apnea severity based on the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI), which measures the number of apneas and hypopneas per hour of sleep. The categories of mild, moderate, and severe apnea based on the AHI scores.
Impact of sleep apnea on overall health: Untreated apnea can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being.The repeated disruptions in breathing can lead to oxygen deprivation, increased stress on the cardiovascular system, and metabolic imbalances.
Cardiovascular risks: The relationship between apnea and cardiovascular problems, such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, heart failure, and stroke. The mechanisms by which apnea contributes to these conditions.
Mental health implications of sleep apnea: The potential impact of apnea on mental health, including an increased risk of depression, anxiety, mood disorders, and cognitive impairment. Sleep deprivation and oxygen deprivation can affect cognitive function and emotional well-being.
Relationship with metabolic disorders in sleep apnea: The link between apnea and metabolic disorders, such as insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. The mechanisms by which apnea can contribute to the development or exacerbation of these conditions.
Treatment Options of Sleep Apnea
Lifestyle modifications: The importance of lifestyle modifications as an initial approach to managing apnea. The role of weight loss and regular exercise in reducing the severity of apnea, as well as the benefits of positional therapy and avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bed.
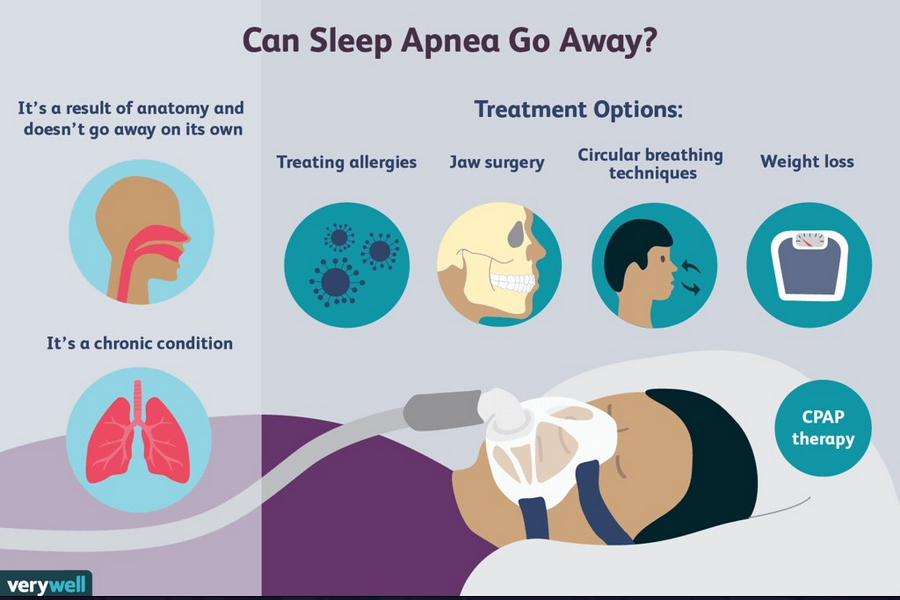
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy: The concept of CPAP therapy, which involves wearing a mask over the nose or both nose and mouth during sleep.CPAP therapy functions by delivering a continuous flow of pressurized air, which helps to maintain an open airway during sleep. Mention the benefits of CPAP therapy and the challenges associated with adherence.
Oral appliances and dental devices: The use of oral appliances and dental devices as an alternative to CPAP therapy. These devices help keep the airway open by repositioning the jaw or tongue.
Surgical interventions: Surgical options for apnea, such as uvulo palato pharyngo plasty (UPPP), which removes excess tissue from the throat, and mandibular advancement devices (MAD), which reposition the jaw to prevent airway obstruction. The potential benefits and considerations for each surgical option.
Emerging and Alternative Treatment Options of Sleep Apnea
Adaptive servo-ventilation (ASV): ASV is a specialized form of positive airway pressure therapy that adapts the pressure based on the individual’s breathing patterns. Its potential use for central apnea or treatment-emergent central apnea.
Hypoglossal nerve stimulation: Hypoglossal nerve stimulation involves the implantation of a device that delivers mild electrical stimulation to the nerves controlling the tongue and upper airway muscles. Its potential benefits for selected individuals with moderate to severe obstructive apnea.
Inspiratory muscle training: Inspiratory muscle training involves exercises to strengthen the muscles involved in breathing. Its potential use as an adjunctive therapy for apnea.
Positional therapy devices: The use of positional therapy devices, such as special pillows or wearable devices, that help individuals maintain a specific sleeping position that reduces airway obstruction. Their potential benefits for individuals with positional obstructive apnea.
Managing Sleep Apnea in Children
Unique considerations for pediatric sleep apnea: The differences in symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment approaches for children with apnea compared to adults. Highlight the importance of addressing apnea in children to support their healthy growth and development.
Diagnosis and treatment approaches for children: The diagnostic methods used for pediatric sleep apnea, such as overnight polysomnography. The treatment options available for children, including lifestyle modifications, CPAP therapy, and surgical interventions.
Coping Strategies and Support
Sleep hygiene tips for better sleep quality: Practical tips for improving sleep hygiene, such as establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a sleep-friendly environment, and practicing relaxation techniques before bed.
Support groups and resources for individuals with sleep apnea: Highlight the availability of support groups, online communities, and educational resources that can provide valuable information, guidance, and emotional support for individuals with sleep apnea and their families.
Conclusion
Importance of early diagnosis and effective treatment: The importance of early detection and appropriate treatment to improve quality of life, reduce the risk of complications, and promote overall health and well-being.
Encouragement for seeking medical help and improving quality of life: Encourage individuals experiencing symptoms of apnea to seek medical evaluation and discuss treatment options with healthcare professionals. Stress the potential benefits of effectively managing apnea in improving sleep quality, overall health, and daily functioning.
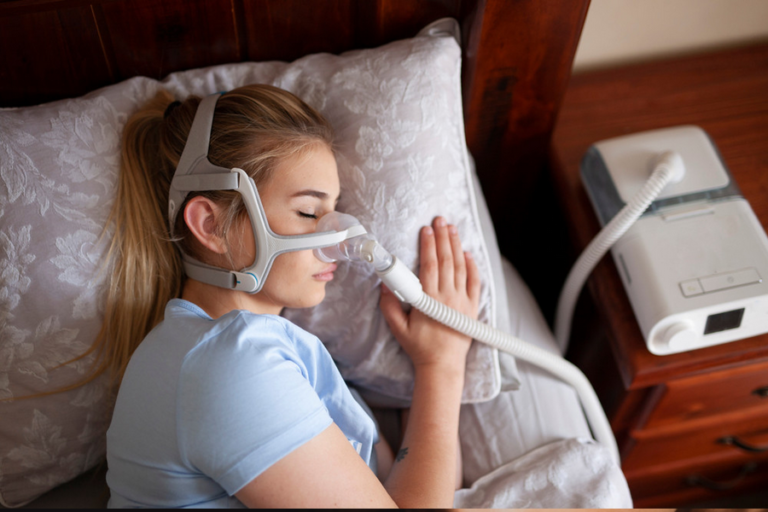






[…] By using a CPAP machine consistently and effectively, it can improve the quality of your sleep and reduce the strain on your body. This, in turn, can help lower your blood pressure levels over time. […]